Products

Buy Crypto

Assets




While our lives are becoming increasingly digitalized and dependent on the likes of centralized platforms such as Google or Meta, critical questions about privacy, owned data, and transparency also arise. Web 3 empowers users once again and makes for safe, transparent, and decentralized interactions. But what is Web 3, and how does it work?
In this guide, you'll learn what Web 3 is, how it's different from earlier versions of the Internet, its core technologies, and its transformational possibilities. Let's dive in and find out what the future of the Internet looks like.
Web 3 is considered by many to be the next generation of the Internet. Its main goal was to give users more control over their online data and interactions. The current web we use in our day-to-day lives relies heavily on tech giants that control our data, often inappropriately, the FTC has reported.
Web 3 runs on decentralized networks powered by blockchain technology. This means users can interact directly without intermediaries, ensuring greater transparency, security, and privacy. In essence, Web 3 focuses on decentralization, user ownership, and open digital ecosystems.
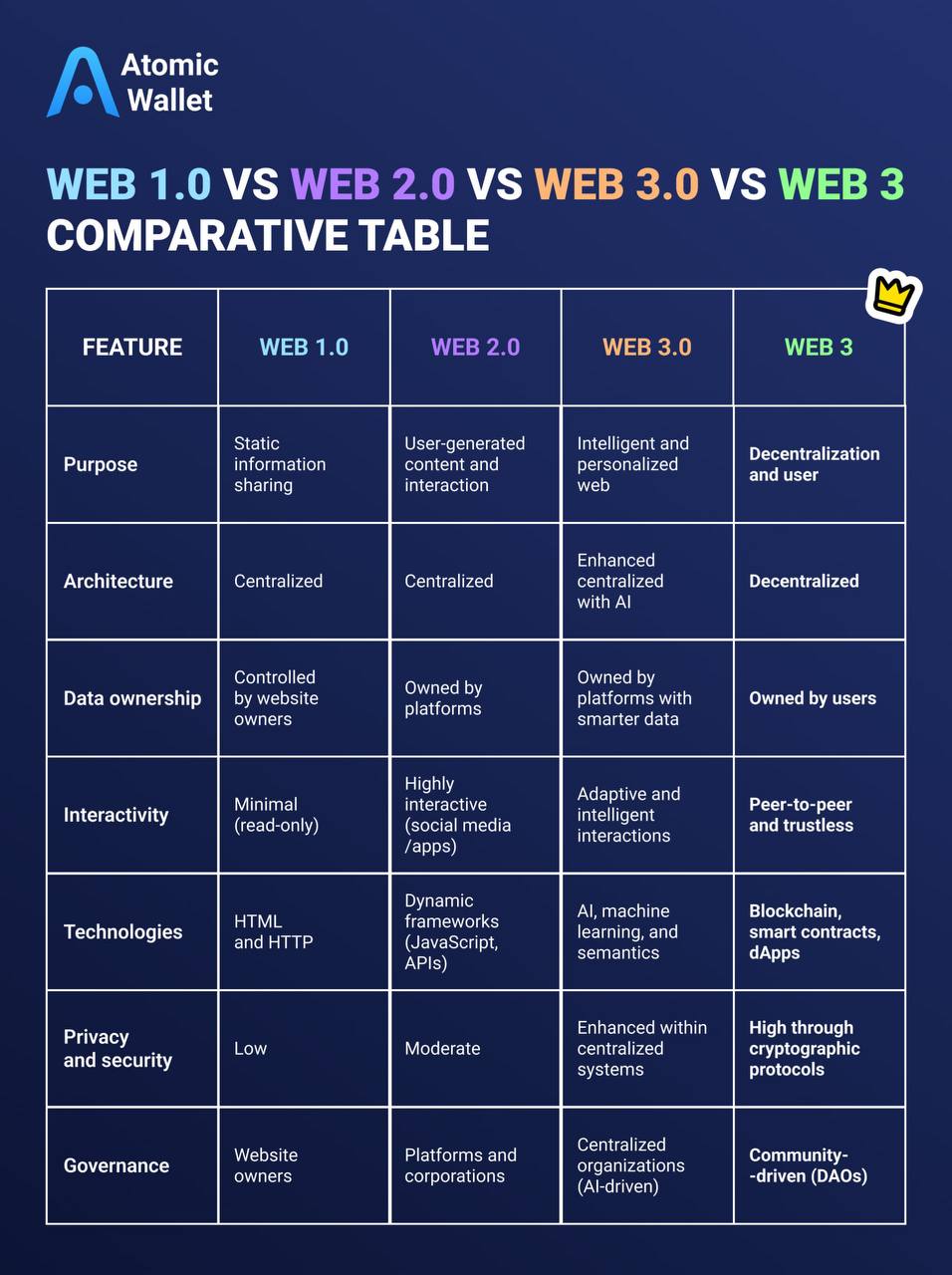
Since its inception, the Internet has undergone a remarkable transformation, going through different phases that define how we interact with information and with each other. Here, we explain each of them so that you can understand this evolution, which is key to appreciating the revolutionary potential of Web 3.
Web 1.0, the first phase of the Internet, emerged in the late 1980s and lasted until the mid-1990s. It is often referred to as the “read-only web.” This era featured static websites designed primarily for information consumption. Users could browse web pages, read articles, and access limited resources, but there was little opportunity for interaction or content creation.
In Web 1.0, websites were simple, centralized, and functioned more like digital brochures. Communication was limited to basic e-mail and text-based forums, and only a few individuals or organizations had the tools to publish content online.
The next phase in this evolution was Web 2.0, which has marked a significant shift towards interactivity and user participation. Since the mid-2000s, platforms such as Facebook and YouTube have allowed users to consume content as well as create and share it. This era has been characterized by the rise of social media, blogs, and collaborative tools, which turned the Internet into a hub of connection and creativity. However, with this interactivity has come centralized control. Large technology companies dominate online platforms and monetize user data for advertising and other purposes.
While Web 2.0 has revolutionized how people interact online, privacy concerns, data ownership, and platform dependency have become more evident.
Web 3.0, often called the “Semantic Web,” envisions an Internet that provides information and understands it. By integrating artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and semantic analysis, Web 3.0 connects data in meaningful ways to deliver more personalized and intuitive user experiences.
Unlike previous versions, Web 3.0 focuses on understanding the context of data. For example, a search query does not simply return results but adapts them based on preferences, location, and relevance, creating a smarter, more adaptive web.
This version of the Internet also aims to reduce fragmentation by enabling a seamless flow of data between platforms, improving accessibility and user convenience. Web 3.0 is less about decentralization and more about making it an intelligent partner in our digital lives.
Web 3 represents the next step in the evolution of the Internet, focusing on decentralization, user empowerment, and trustless systems.
The term “Web3” was coined in 2014 by Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, during discussions about creating a more decentralized, user-controlled online ecosystem. Wood envisioned Web3 as a blockchain-based Internet in which intermediaries are unnecessary, and users retain full ownership of their data and digital interactions.
In contrast to other versions of the web, Web 3 leverages blockchain technology to create a user-governed Internet, emphasizing privacy, security, and individual ownership of data. In this decentralized web, users are no longer passive participants or dependent on centralized platforms. Instead, they control their identities and digital assets through decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, cryptocurrencies, and peer-to-peer interactions.
Key innovations such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) define this phase, making Web 3 not just an upgrade but a complete rethinking of how we interact online.

Web 3 and Web 3.0 are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they represent distinct ideas in the evolution of the Internet. Although both aim to innovate the way we interact online, their goals, technologies, and architectures differ significantly.
Web 3.0 focuses on enhancing data connectivity and improving the user experience. Using semantic technologies and artificial intelligence, it succeeds in making the Internet smarter and more personalized by understanding the context of data.
In contrast, Web3 emphasizes decentralization and user control through blockchain technology to return data ownership to individuals and create a trustless peer-to-peer digital environment.
Let's examine each type of web's main differences, showing its unique characteristics, purposes, technologies used, and more.
Web 3 powers decentralized financial systems, transforming the way we interact with money and assets online. This type of web allows users to trade cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, own digital assets such as NFT, and access financial tools without relying on banks or intermediaries.
Transactions are processed securely and transparently through smart contracts, ensuring trustless interactions. This decentralized approach gives users full control over their assets, reduces costs and opens financial services to a global audience, fostering inclusion and innovation in the digital economy.
Web 3 is built on transformative technologies that enable decentralization, security, and user empowerment. Let’s break them down simply.
Blockchain is the foundation of Web 3. It’s a system that records information in a way that is secure, transparent, and cannot be changed. Instead of storing data on one central server, blockchain spreads it across many computers (nodes). This makes it nearly impossible to tamper with.
What makes blockchain revolutionary in Web 3 is its ability to replace trust in centralized authorities (like banks or tech companies) with trust in code. For example, instead of relying on a bank to verify a transaction, the blockchain verifies it through its network of nodes. This ensures fairness and transparency without needing intermediaries.
Smart contracts are like digital instructions that execute themselves automatically when certain conditions are met. They run on the blockchain, making them tamper-proof and reliable.
For example, if you’re selling an item online, a smart contract can release payment to you automatically once the buyer confirms receipt. In Web 3, smart contracts are used for everything from managing loans, trading assets, or even selling NFTs. Their efficiency reduces costs and eliminates the need for lawyers or middlemen in many transactions.
Digital assets are anything you own online, such as cryptocurrencies like Solana or Cardano, or non-fungible tokens, representing unique digital items like art, music, or collectibles.
NFTs go beyond ownership, creating new ways for users to participate in Web 3 ecosystems. For instance, gamers can own in-game items that they can sell or trade outside the game. Artists can sell their creations digitally and even earn royalties each time their work is resold.
These assets aren’t controlled by platforms like in Web 2.0. Instead, they are entirely yours, stored securely on the blockchain.

Web 3 is revolutionizing a multitude of industries by introducing decentralized, user-controlled systems that challenge traditional ways of operating. Below we explore some of their real-world use cases and how they are shaping the future of our digital interactions.
DeFi has transformed traditional financial systems by eliminating intermediaries such as banks and enabling direct financial services between users. Through blockchain-powered platforms and smart contracts, users can lend, borrow, trade, and earn interest on their digital assets in a secure, transparent, and automated way.
One example is Aave, which allows individuals to earn passive income by lending cryptocurrency. Another well-known example in the crypto ecosystem is Uniswap, which allows users to trade assets directly without centralized exchanges.
These innovations highlight how decentralized finance is democratizing access to financial services around the world.
NFTs have unlocked new opportunities for creators and collectors by tokenizing digital and physical assets. Artists can directly monetize their works while retaining ownership, and buyers get verifiable, tamper-proof proof of ownership.
Beyond art, NFTs are now being used in the gaming, music, and ticketing sectors, among many others. For example, the record-breaking sale of digital artist Beeple's NFT “Every day: The First Five Thousand Days” demonstrated 2021 the potential of this technology.
Other top brands, such as Coca-Cola, Adidas, and Samsung, are also leveraging NFTs to engage with their customers by offering unique digital collectibles.
The gaming industry has embraced Web 3 by allowing players to own and trade game assets, enabling real-world economic opportunities. \Unlike traditional games, where companies retain ownership of objects, blockchain-based games allow players to have full control.
Axie Infinity exemplifies this shift, as players can earn cryptocurrencies by playing and participating in its economy. Similarly, virtual worlds such as Decentraland allow users to buy, sell, and develop virtual real estate, merging creativity with economic incentives.
DAOs redefine organizational management by enabling decentralized governance. Decisions are made collectively by members, eliminating the need for centralized authority.
These organizations rely on smart contracts to enforce rules and execute decisions transparently. For example, Friends With Benefits DAO demonstrates how community-driven initiatives can fund creative projects, with members having a direct voice in their direction.
This model is creating a new era of collective ownership and accountability.
Web 3 technologies are streamlining supply chains by improving traceability and transparency. Blockchain enables real-time tracking of goods, reducing fraud and inefficiencies.
IBM Food Trust is a good example: food products are tracked from farm to fork, guaranteeing their quality and authenticity to consumers. This use case is especially important in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, luxury goods and agriculture, where trust and provenance are critical.
Web 3 is changing social media by giving users control over their data and allowing them to monetize their content directly. Unlike traditional platforms, which profit from user-generated content and data, decentralized platforms like Lens Protocol allow users to own their profiles and posts.
This shift solves privacy issues while fostering a fairer exchange of value between platforms and their users, redefining the way we connect and share online.
Managing online identities securely is a major challenge on the centralized web. Web 3 introduces decentralized identity solutions, which allow users to own and manage their personal data without relying on corporations.
Ethereum Name Service (ENS), for example, allows users to create blockchain-based usernames linked to their wallets, providing a unified and private digital identity. This technology ensures that users maintain control over their data, reducing risks such as identity theft.
A Web 3 wallet is a digital tool that allows users to securely store, manage, and interact with cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based services. Web 3 wallets are designed for the decentralized Internet and offer features such as:
One of the most prominent wallets in the Web 3 space is Atomic Wallet, which checks greatly all of the above. Compatible with more than 1,000 cryptocurrencies, Atomic Wallet is widely recognized for its robust features and user-friendly design. In addition, Atomic Wallet offers integrated cryptocurrency exchange functions and staking to earn rewards on supported assets.
Follow these simple steps to set up Atomic Wallet and start exploring Web 3:

Web 3 offers a transformative vision of the Internet, but it also poses some challenges. Let’s analyze its main advantages and disadvantages to provide a balanced perspective.
Web 3 introduces innovative security measures, such as decentralization and cryptography, that make it more resistant to hacking and data breaches than traditional systems. Since data is stored in a network of nodes rather than on a central server, tampering or unauthorized access is much more difficult.
However, Web 3 shifts much of the responsibility to the users. Protecting private keys is crucial, as losing them could mean losing permanent access to funds and data. Phishing attacks and scams targeting unsuspecting users are also common in the decentralized landscape. Therefore, user vigilance and the use of trusted wallets, such as Atomic Wallet, are critical to navigating the Web 3 space safely.
Web 3 has tremendous potential and is steadily gaining traction, with recent developments across various industries demonstrating its transformative possibilities.
In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, Fastex is spearheading Web 3 advancements by introducing cutting-edge blockchain solutions and organizing initiatives like the Harmony Meetup VI to promote blockchain adoption and education. The fashion industry is also integrating Web 3 technologies. Designer Kate Barton, in collaboration with Syky, launched a "phygital" product—a handbag available both as a physical item and as a NFT.
Additionally, Binance recently launched Binance Alpha, a platform designed to showcase emerging Web 3 and crypto projects. These developments underscore Web 3's expanding influence and potential to redefine digital landscapes, fostering a more decentralized and user-centric Internet.
Web 3 is already reshaping the Internet to incorporate decentralization, user power, and transparency into today's digital life.
Its penetration in sectors such as financial services, supply chains, and even fashion demonstrates its transformative power. These are not science fiction concepts but are now finding their application in practice. They portend a time when technology will be integrated into our lives.
Scalability, ease of use, and user onboarding remain major hurdles to these benefits; however, all this continuous improvement of emerging technologies in Web 3 hints at a future where people are in charge of their data and digital things.
The mature phase of Web 3 promises a retranslation of how the Internet works, which will be driven by user ownership and open innovation towards security, inclusion and equity in the digital realm.

Explore the Crypto Fear and Greed Index to enhance your trading strategies and market decisions. Learn more now!